Children with Autism Process Auditory Information Differently

A team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, examined specific aspects of auditory perception in children with autism. The scientists observed atypical alpha rhythm activity both during sound perception and at rest. This suggests that these children experience abnormalities in the early stages of sound processing in the brain's auditory cortex. Over time, these abnormalities can result in language difficulties. The study findings have been published in Brain Structure and Function.
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are a group of conditions caused by abnormalities in brain development that can affect communication skills and social behaviour. Children with ASD often experience co-occurring language impairments, ranging from mild language deficits to a complete inability to speak.
The causes of language impairment in ASD are not yet well understood. Researchers believe that the neurobiological mechanisms of autism stem from an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory processes in the cerebral cortex, driven by oscillations of nerve cells in the brain. These oscillations produce weak but detectable electromagnetic signals, such as alpha, beta, and gamma rhythms, which can be measured using magnetoencephalography (MEG).
An international team of researchers, including scientists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, studied alpha rhythm oscillations (markers of excitability) in children with autism. Alpha rhythms play a key role in processing sensory information and maintaining attention, eg during auditory perception.
The scientists explored the relationship between sound perception and language impairment in children with ASD. To achieve this, they used magnetoencephalography to measure brain activity in 20 children with autism of varying severity and in 20 typically developing controls. All study participants underwent clinical and behavioural language assessments, as well as tests for nonverbal intelligence (IQ) and the severity of autistic traits. Their language skills were measured using RuCLAB (Russian Child Language Assessment Battery). During the MEG, participants were presented with sound stimuli while their brain activity was measured, requiring no special actions from them. The authors of the experiment monitored alpha oscillations both at rest and during the processing of presented audio signals.
It was found that children with autism exhibit impaired alpha rhythms both during auditory perception and at rest. Typically, when sounds are processed in the auditory cortex, the power of alpha waves decreases significantly, while it increases during rest. The opposite pattern was observed in children with autism.
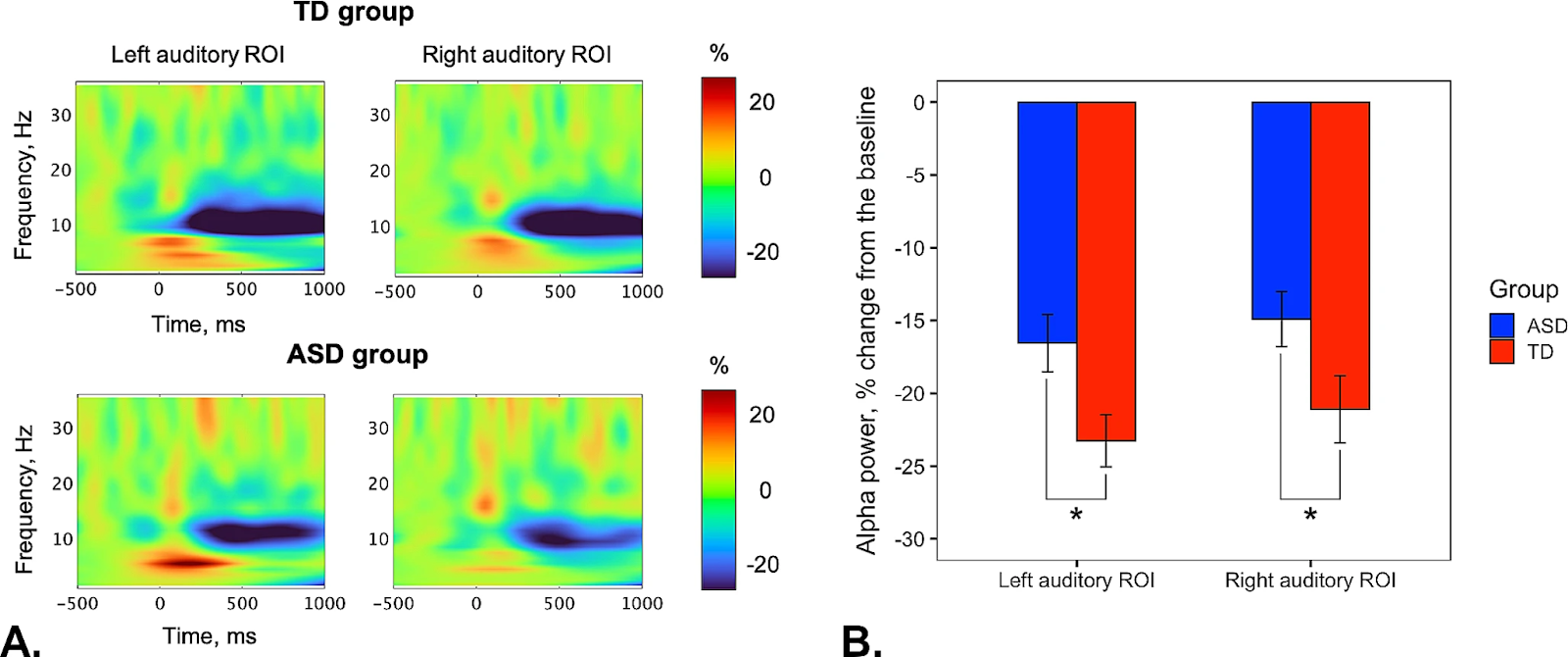
'A slight decrease in alpha rhythm power during auditory information processing in children with autism indicates increased excitability of neural networks in the auditory cortex, confirming an imbalance between excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex,' explains Vardan Arutiunian, co-author of the study and research fellow at the Seattle Children's Research Institute, USA.
The authors of the paper also found a link between brain activity at rest in the left auditory cortex and the language abilities of children with ASD. The researchers converted the complex, multidimensional MEG signals into a set of parameters, analysed them, and discovered that one component of the signal (offset), which reflects the average frequency of neural discharges, is associated with language skills. The higher this parameter (and consequently, the greater the resting neural excitability in the left auditory cortex), the poorer the language skills of children with ASD.

Olga Dragoy
'We analysed all the data collected during the experiment, including the MEG results, IQ tests, and assessments of autistic traits and language skills. It was found that children with more impaired neural processes in the left hemisphere exhibited poorer language abilities. We observed that in autism, abnormalities are present at the early stages of information processing in the auditory cortex, which can impact higher-level processes such as language,' according to Olga Dragoy, Director of the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
The study's findings can lead to a better understanding of the causes of language impairment in autism spectrum disorders and contribute to the development of corrective interventions.
See also:
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.
Physicists at HSE University Reveal How Vortices Behave in Two-Dimensional Turbulence
Researchers from the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the HSE University's Faculty of Physics have discovered how external forces affect the behaviour of turbulent flows. The scientists showed that even a small external torque can stabilise the system and extend the lifetime of large vortices. These findings may improve the accuracy of models of atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The paper has been published in Physics of Fluids.
Solvent Instead of Toxic Reagents: Chemists Develop Environmentally Friendly Method for Synthesising Aniline Derivatives
An international team of researchers, including chemists from HSE University and the A.N. Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS), has developed a new method for synthesising aniline derivatives—compounds widely used in the production of medicines, dyes, and electronic materials. Instead of relying on toxic and expensive reagents, they proposed using tetrahydrofuran, which can be derived from renewable raw materials. The reaction was carried out in the presence of readily available cobalt salts and syngas. This approach reduces hazardous waste and simplifies the production process, making it more environmentally friendly. The study has been published in ChemSusChem.
How Colour Affects Pricing: Why Art Collectors Pay More for Blue
Economists from HSE University, St Petersburg State University, and the University of Florida have found which colours in abstract paintings increase their market value. An analysis of thousands of canvases sold at auctions revealed that buyers place a higher value on blue and favour bright, saturated palettes, while showing less appreciation for traditional colour schemes. The article has been published in Information Systems Frontiers.